NEWS&EVENTS
After sorting, crushing, screening, roasting and other treatments, waste lead-acid batteries can be used to obtain lead-containing recycled lead. These treated lead-containing materials can be smelted in rotary furnaces and refining furnaces to produce products such as lead ingots.
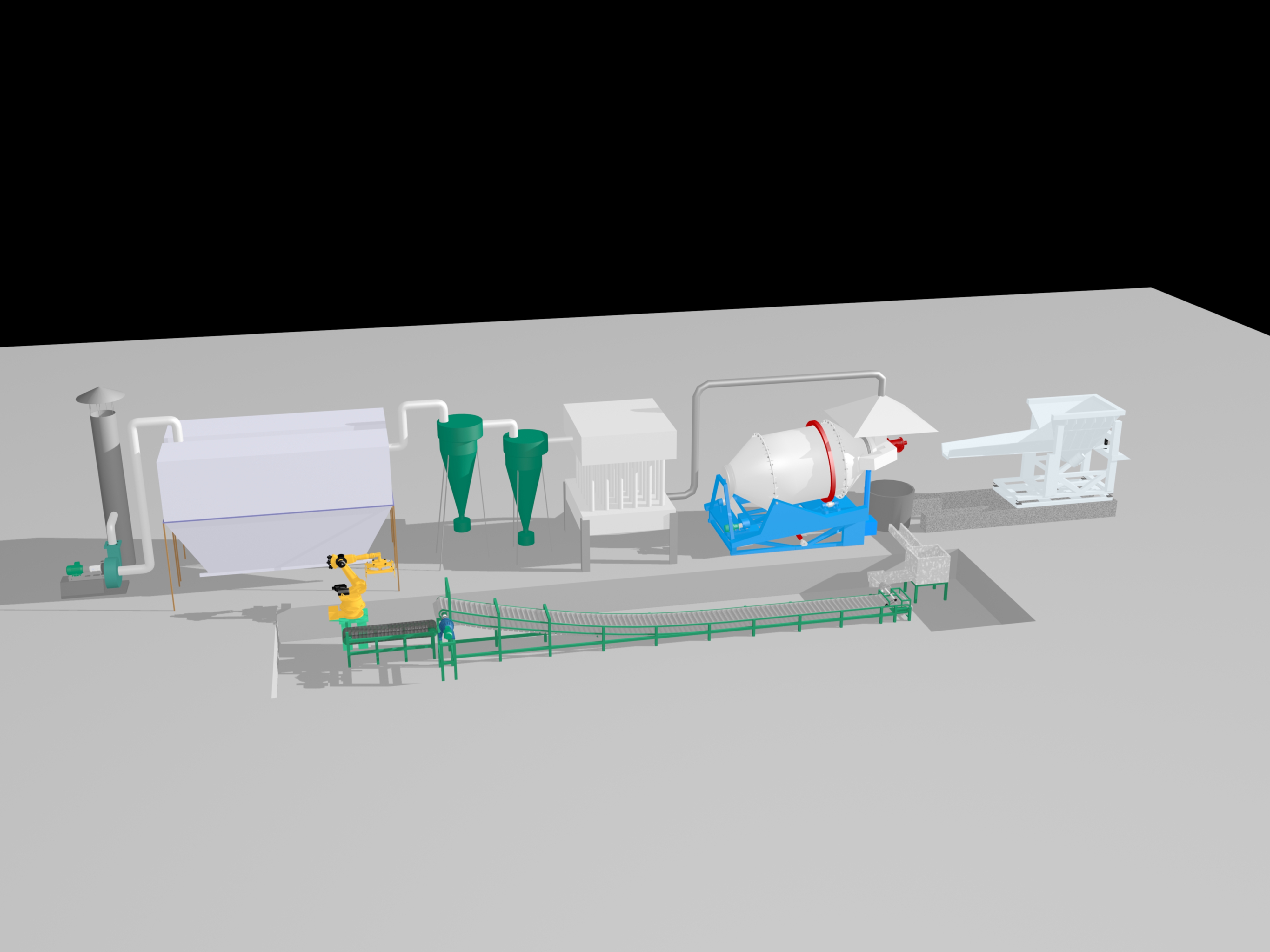
The lead-acid batteries are crushed, and the crushed materials are screened to remove oversized or undersized particles to form shells, lead mud, and lead plates. The screened materials are roasted at about 500°C to oxidize the residual organic matter and discharge it.
The roasted lead mud and lead plate are placed in a rotary furnace for smelting. In the furnace, the material reacts with the oxidant to oxidize the lead into lead oxide and form lead slag. At the same time, some harmful gases such as sulfur dioxide are also produced. The lead slag is placed in a refining tank for refining. In the refining tank, reducing agents such as coke and charcoal are added to reduce the impurities and precipitate to the bottom. At the same time, some harmful gases such as carbon monoxide are also produced. The refined material is roasted again so that the residual organic matter is oxidized and discharged. The re-roasting temperature is generally around 500°C.
The re-roasted material is placed in a refining furnace for re-refining. The re-refined material is cast into recycled lead blocks or other forms of products.
Through multiple steps such as crushing, roasting, lead smelting in a rotary furnace, and refining in a refining furnace, the recycled lead smelting process can recycle waste lead products and obtain recycled lead products with a purity of up to 99.99%. At the same time, during the entire process, attention should be paid to the treatment and discharge of harmful gases to protect the environment and human health.